Paper
Evolution of Methods for the Oxidation of Primary Alcohols to Carboxylic Acids: From Metal Oxides to Biocatalysis
J. Spang, F. Mascia, W. Kroutil
JACS Au 2026, 6, 659-677
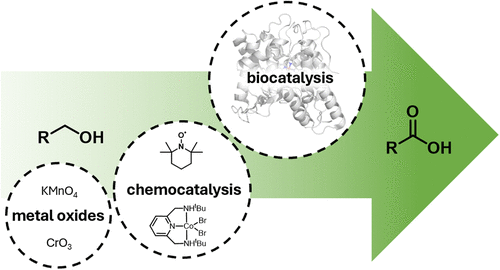
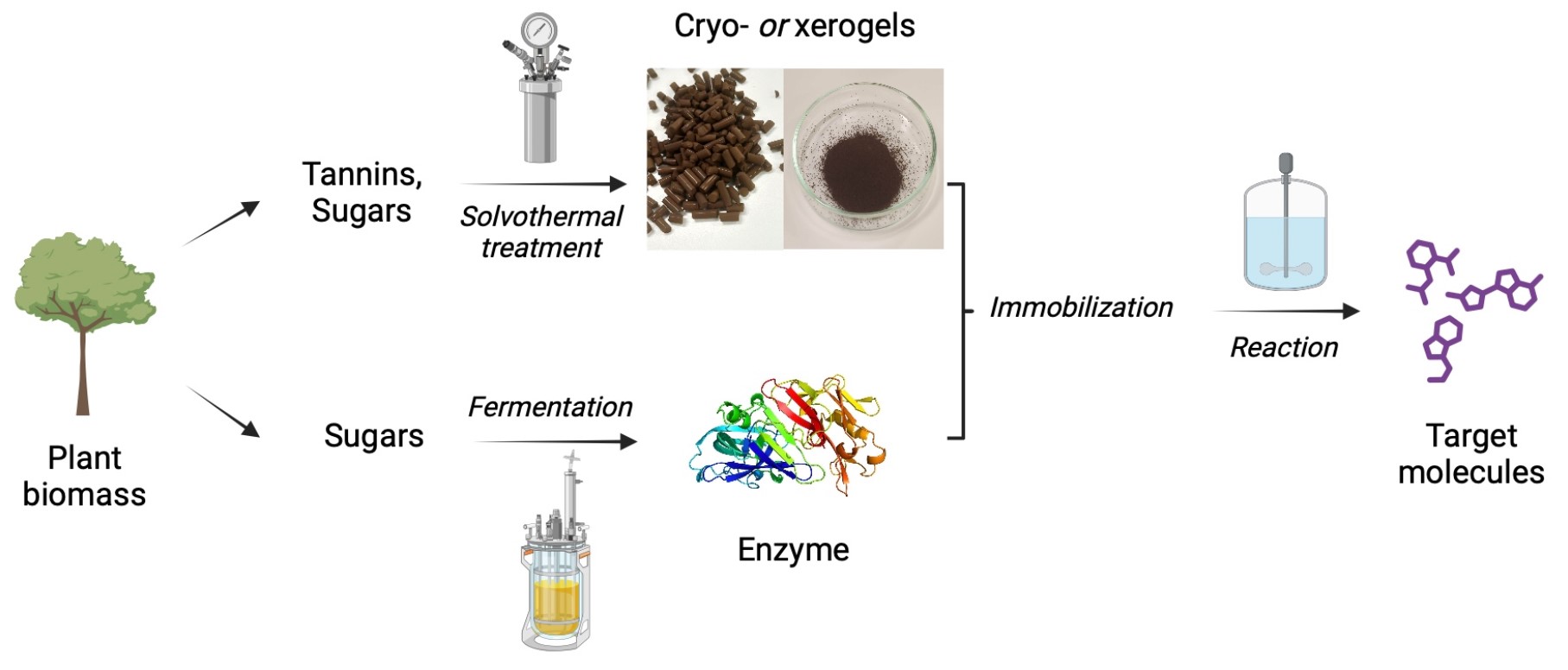
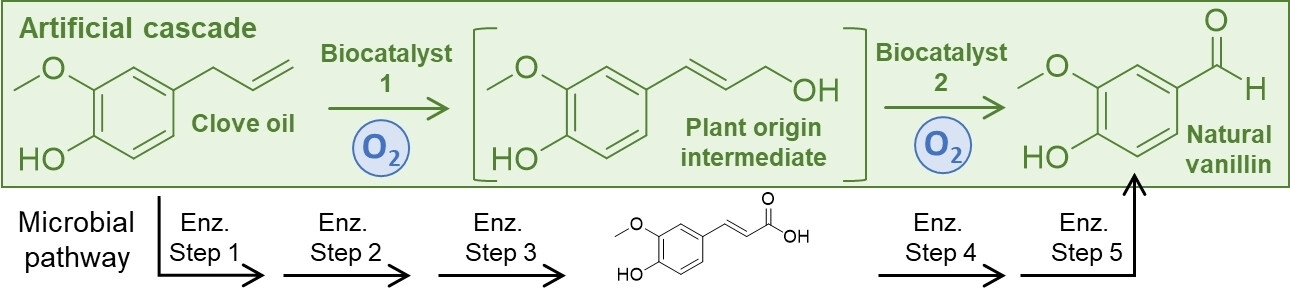
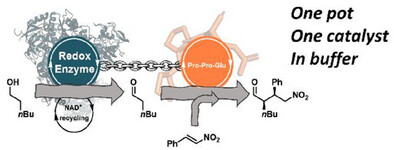
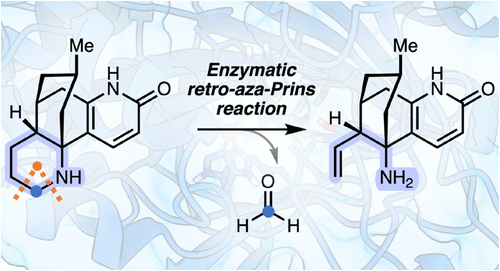
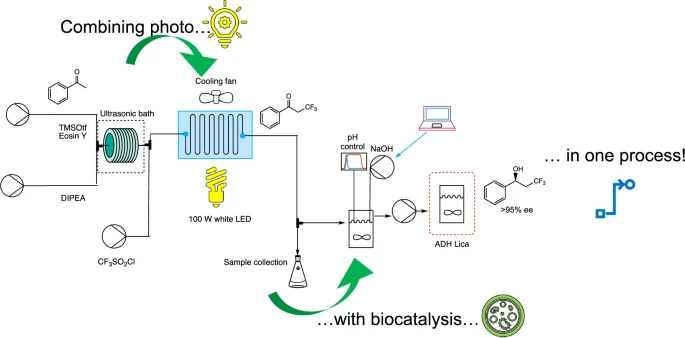
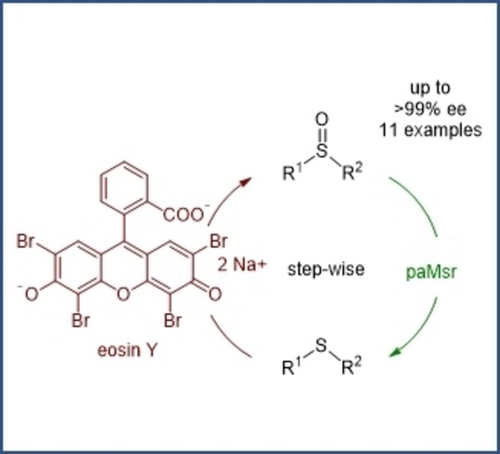
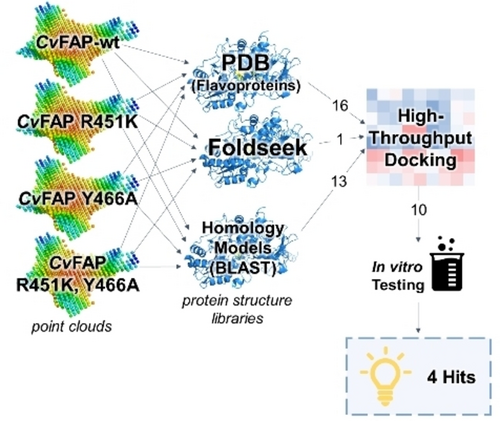
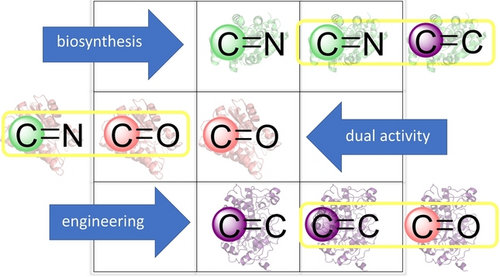
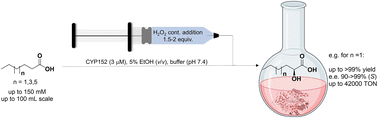
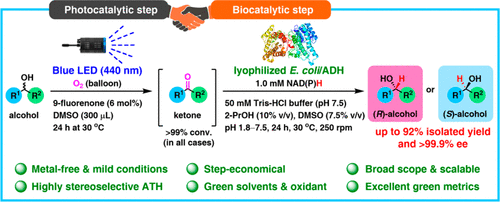
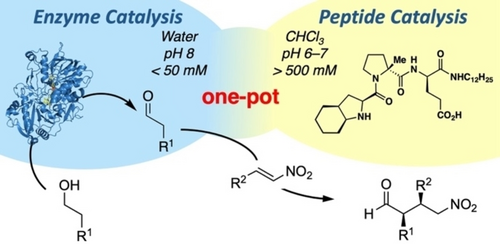
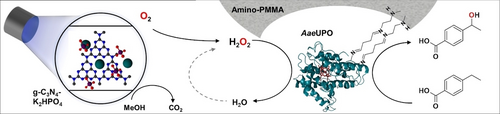
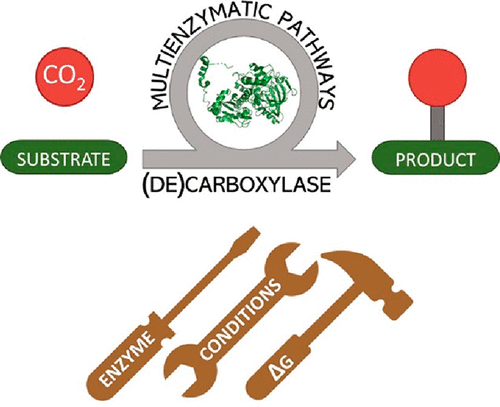
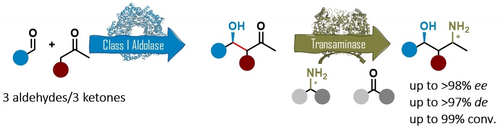
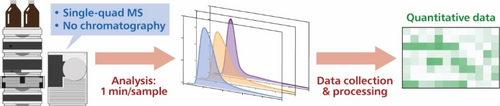
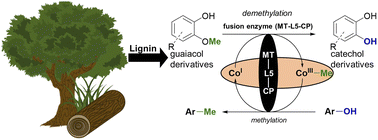
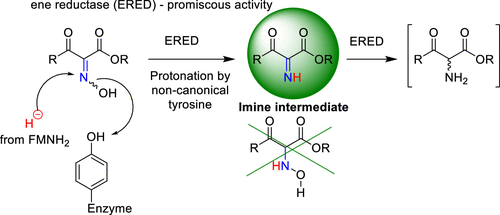
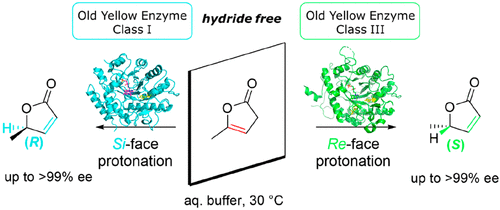
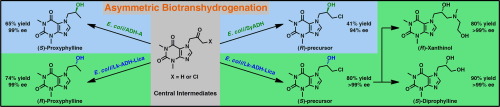
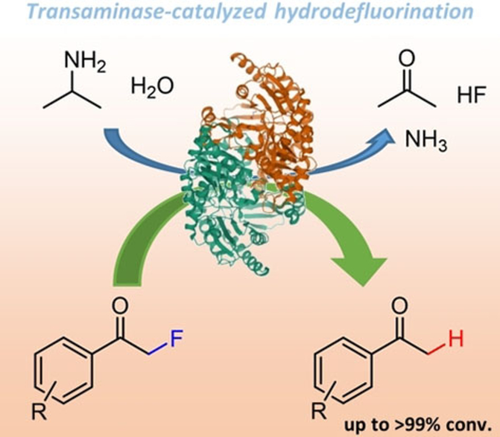
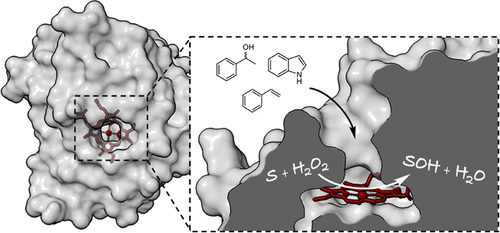
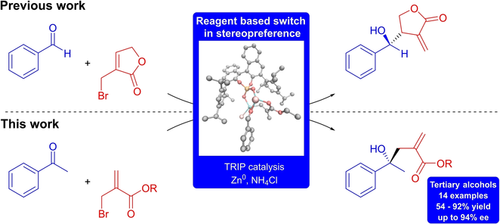
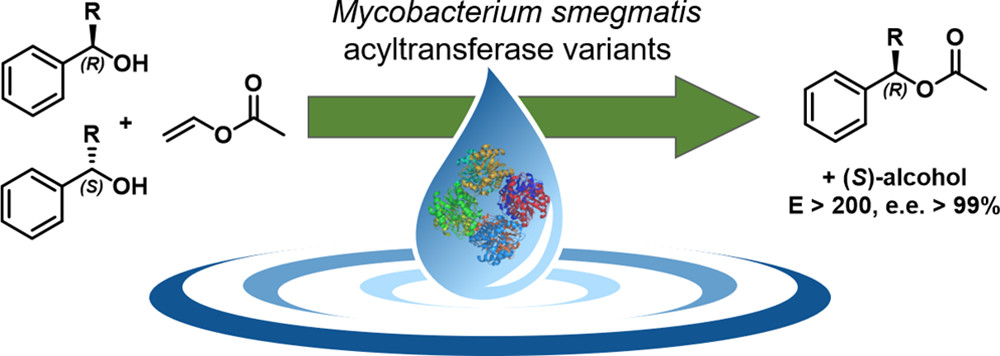
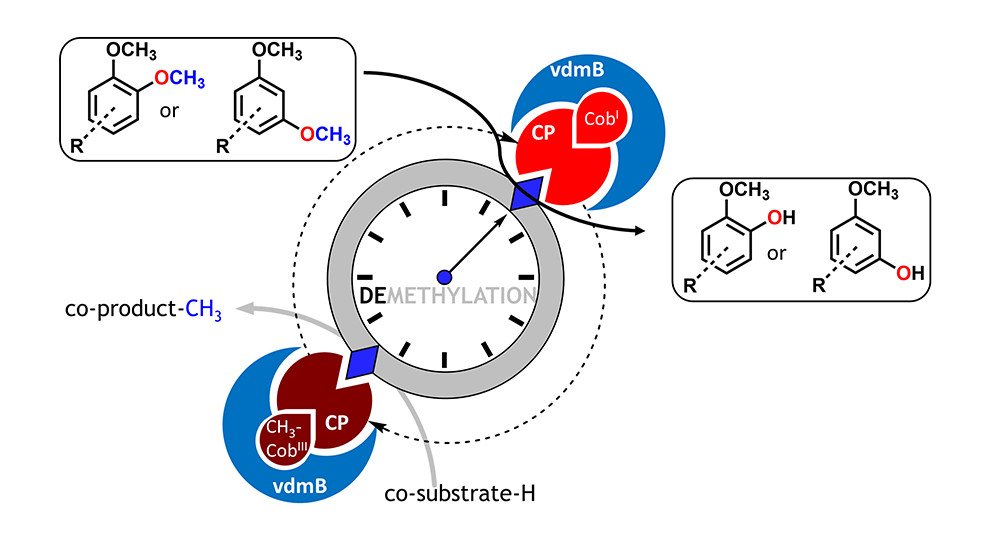
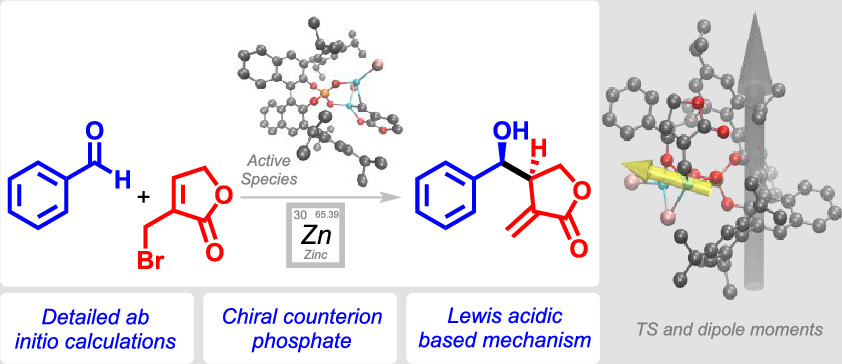
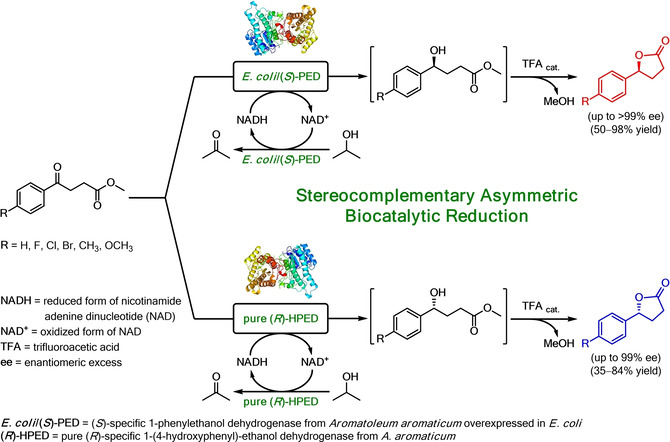
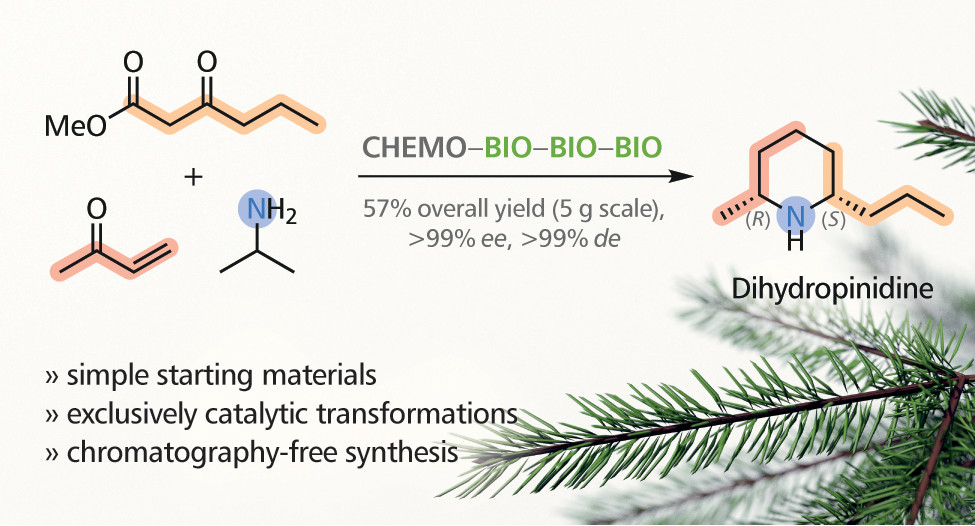
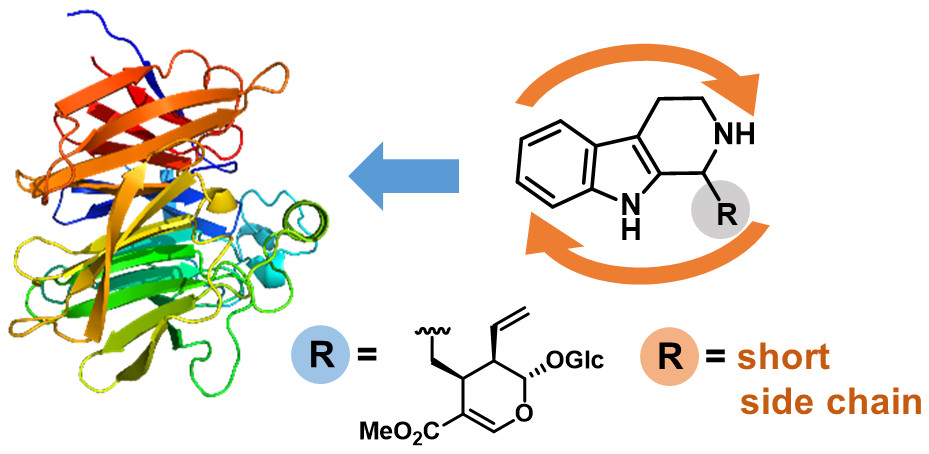
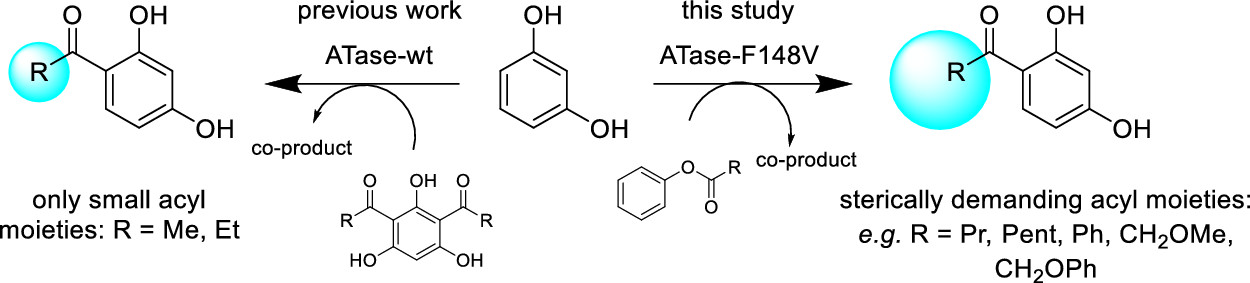
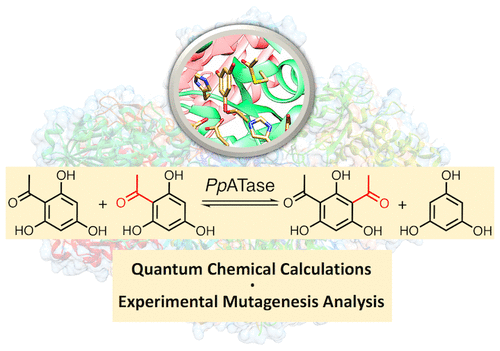
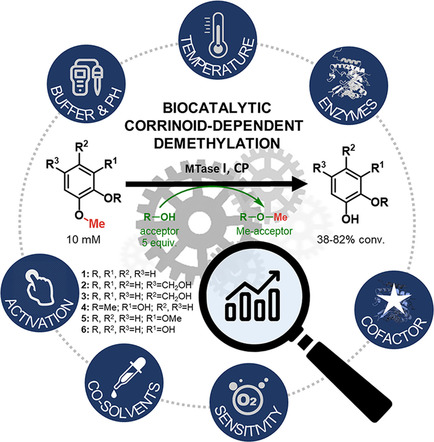
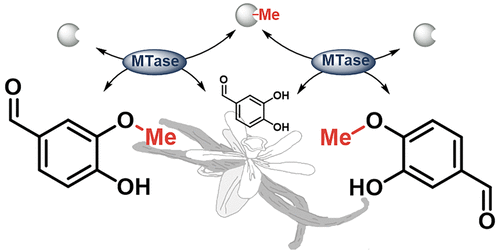
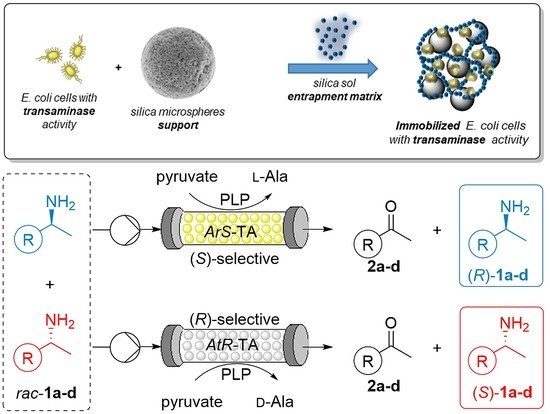
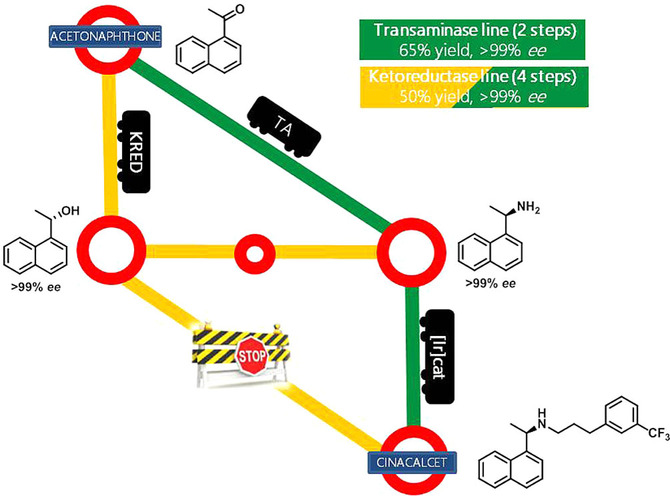
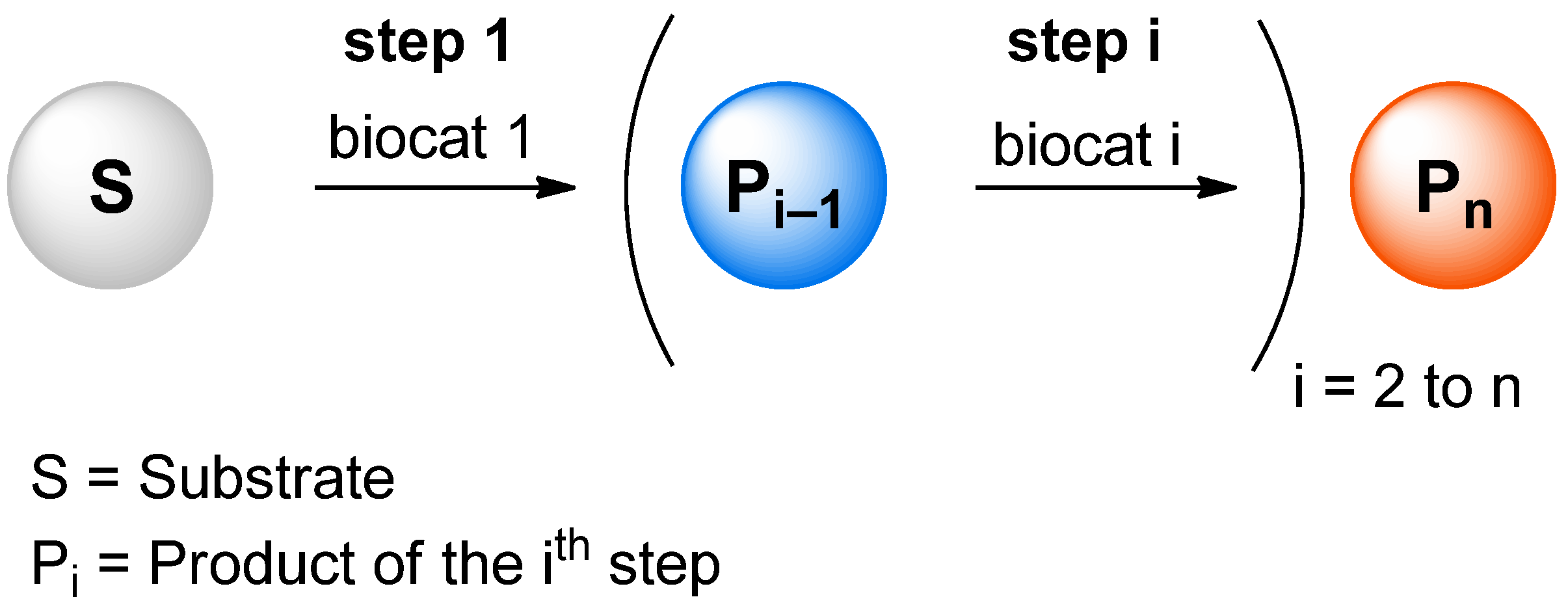
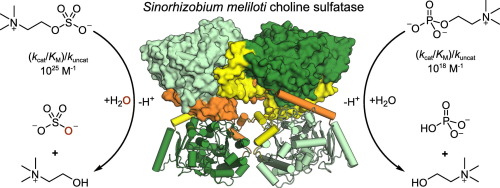
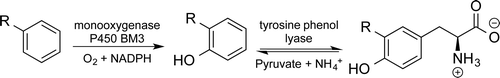
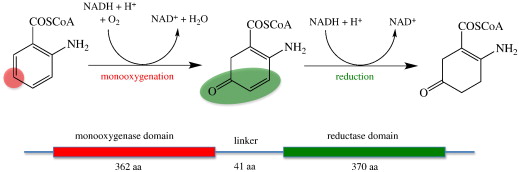
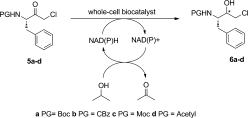
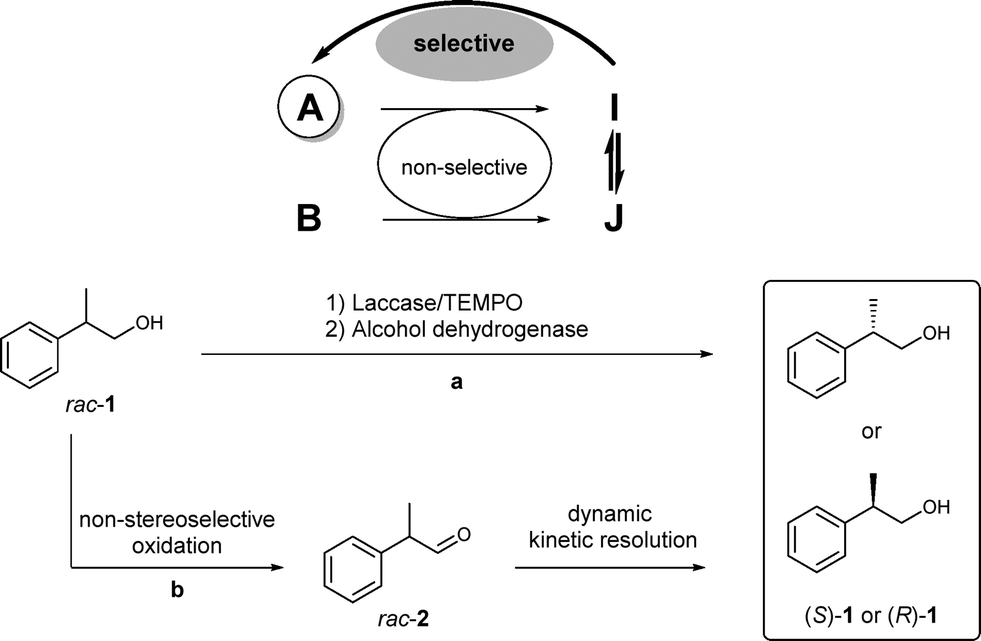
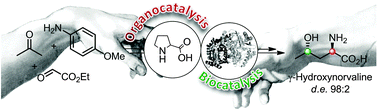
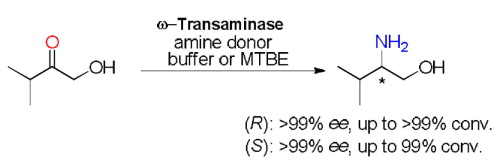
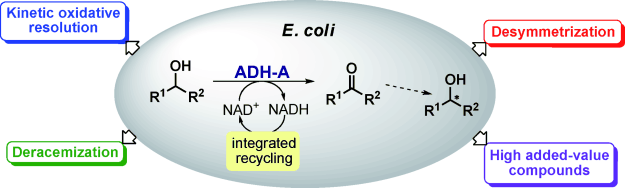
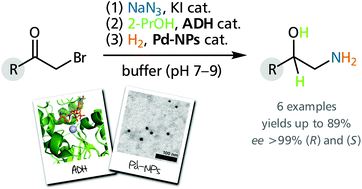
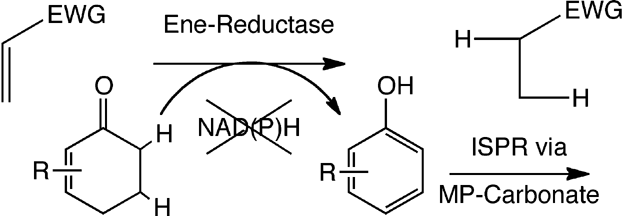
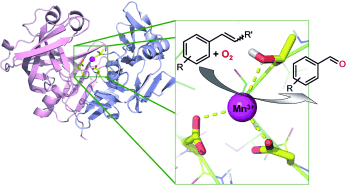
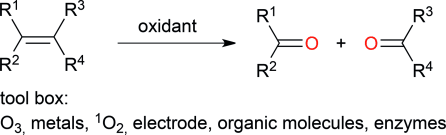
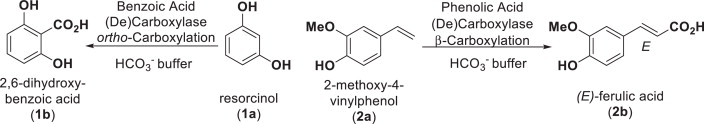
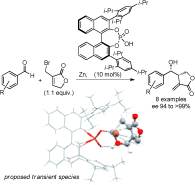
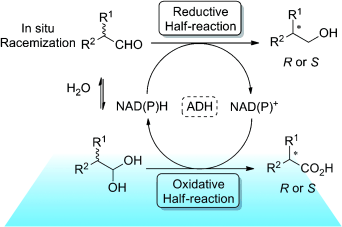
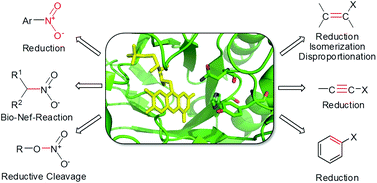
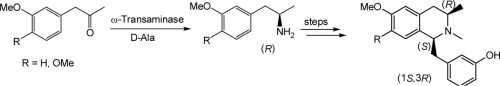
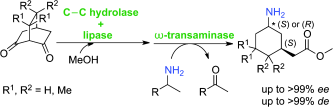
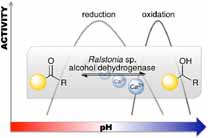
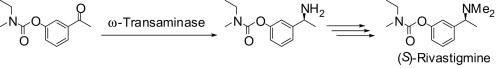
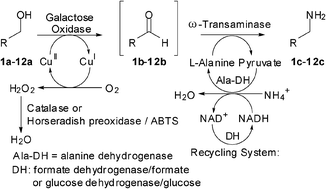
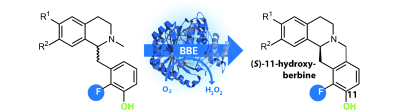
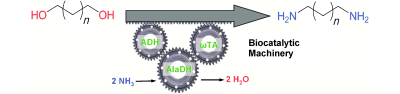
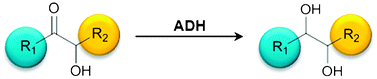
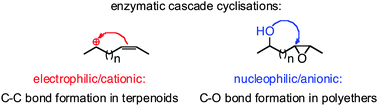
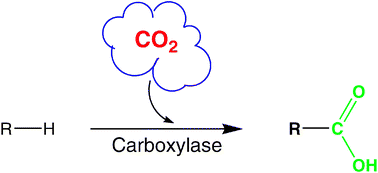
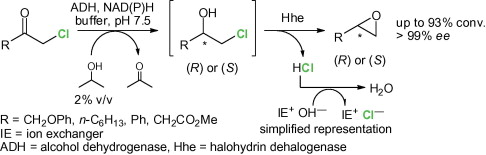
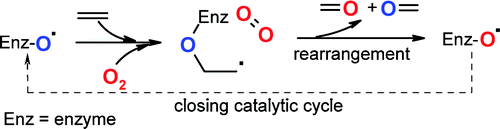
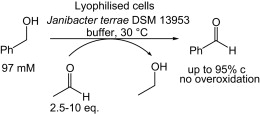
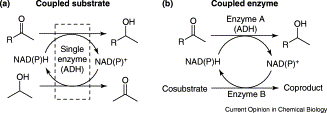
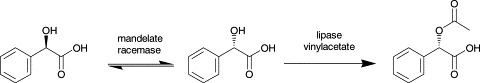
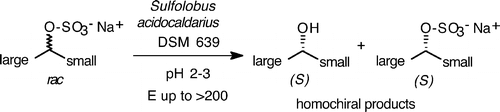
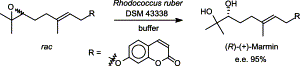
Carboxylic acids are central building blocks in fine chemical synthesis. Although the direct oxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids appears straightforward from a retrosynthetic perspective, it is often associated with significant challenges. In this Perspective, we discuss concepts of one-pot approaches for the oxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids. These approaches are grouped into chemical and biocatalytic concepts, which are structured according to the stoichiometric oxidant employed. The evolution of these methods is traced from traditional chemical oxidations to modern catalytic and biocatalytic strategies, underscoring the parallel shift in oxidant selection and the resulting improvements in selectivity, practical utility, and sustainability.


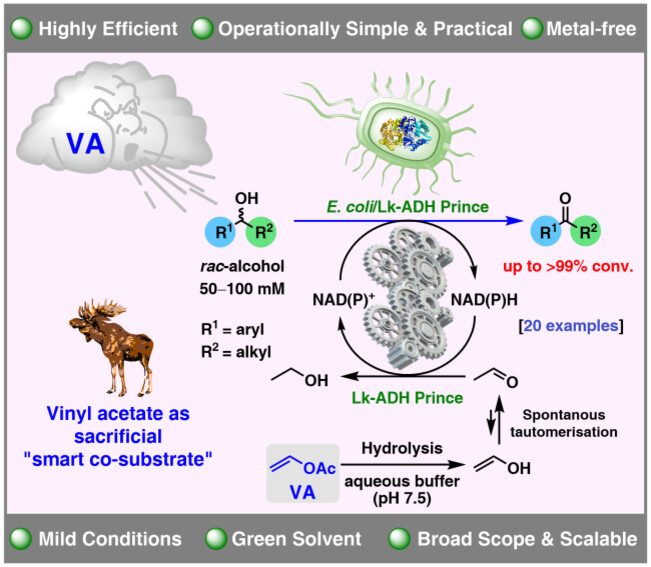
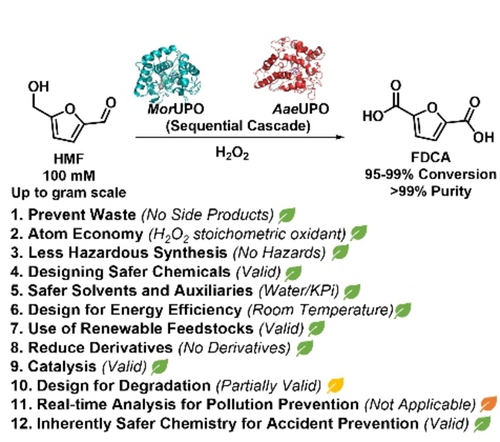
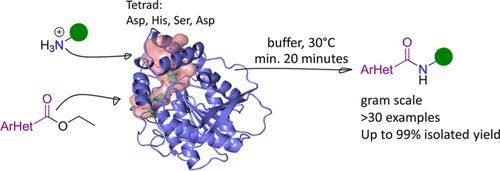
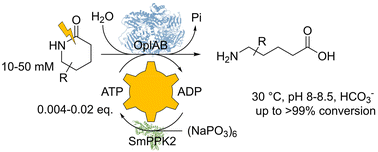
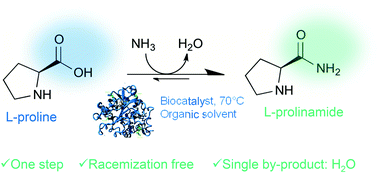
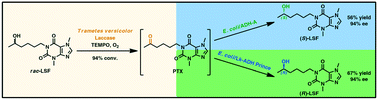
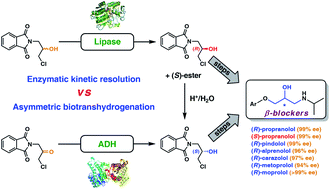
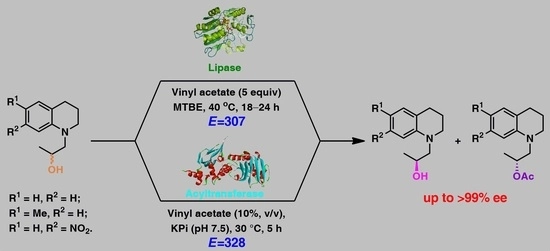
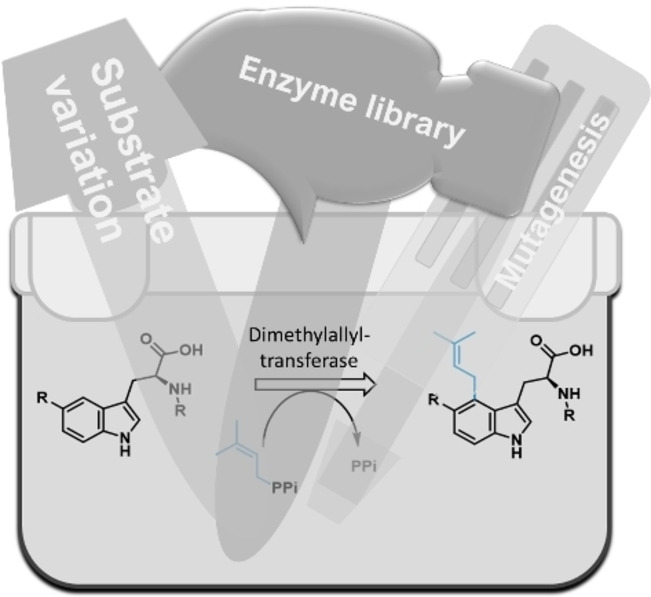
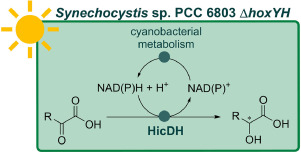

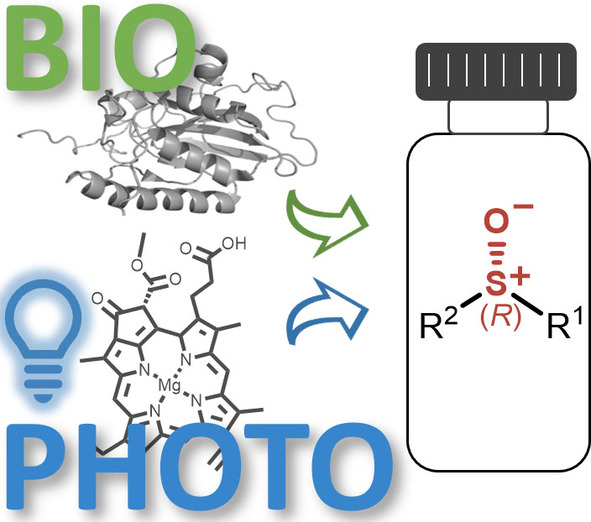
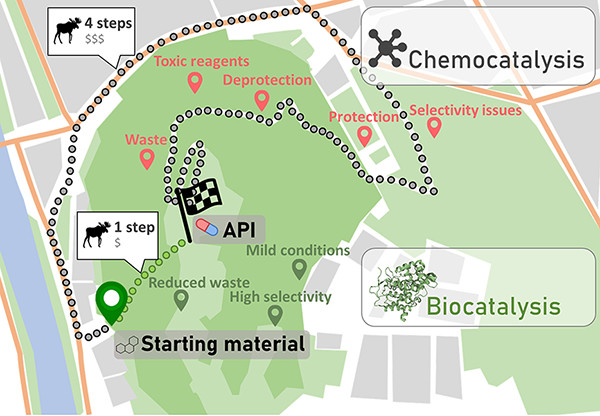
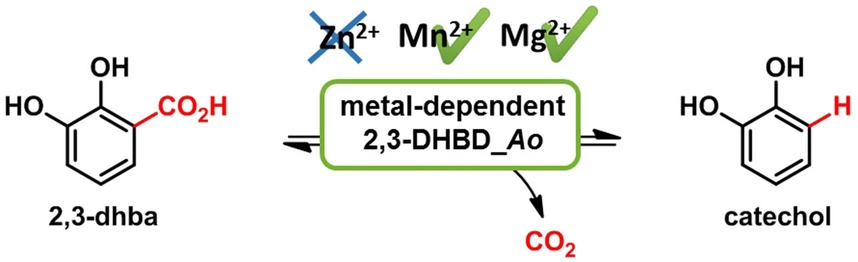
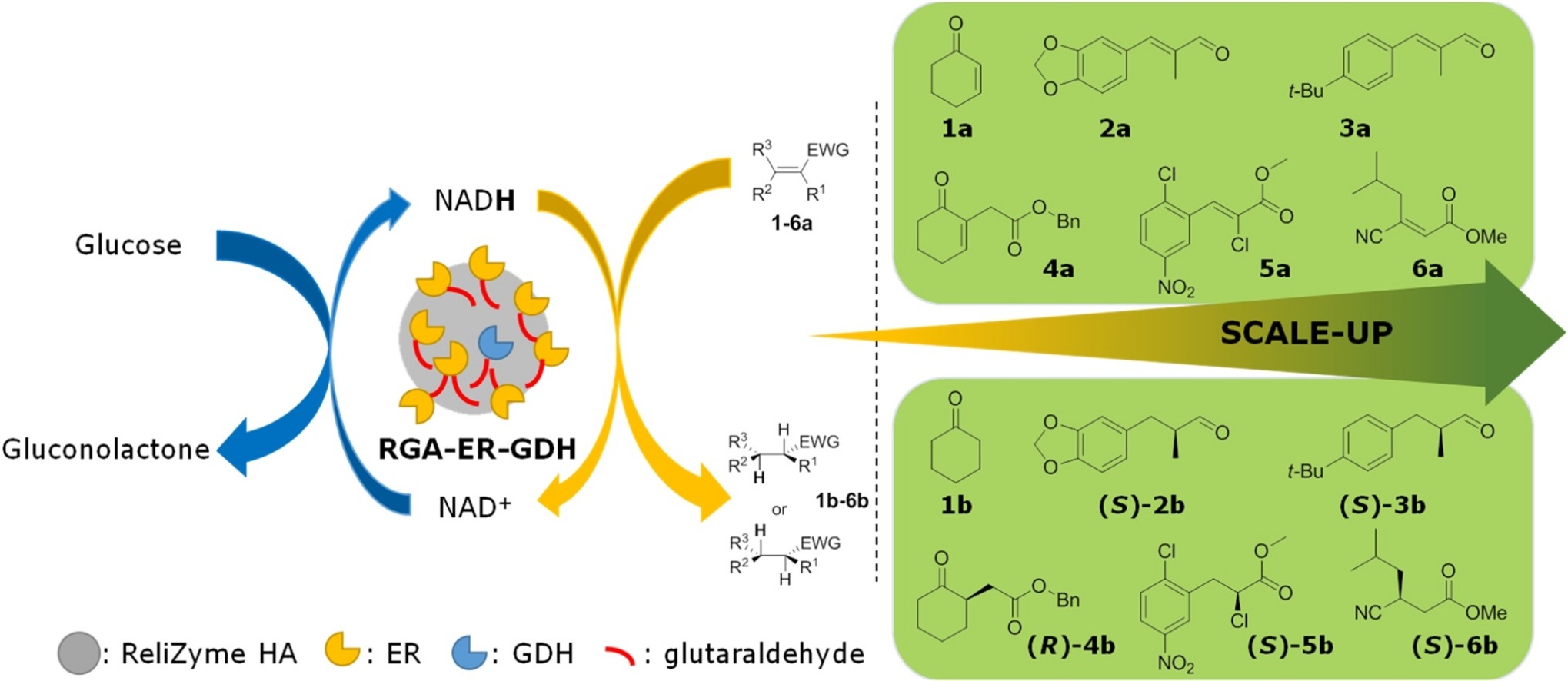
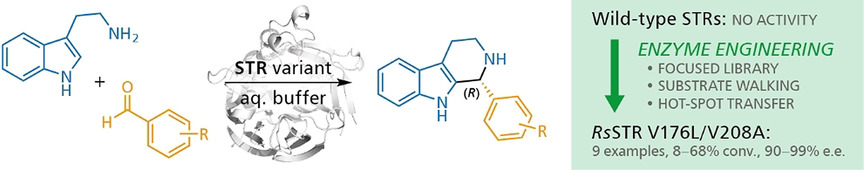
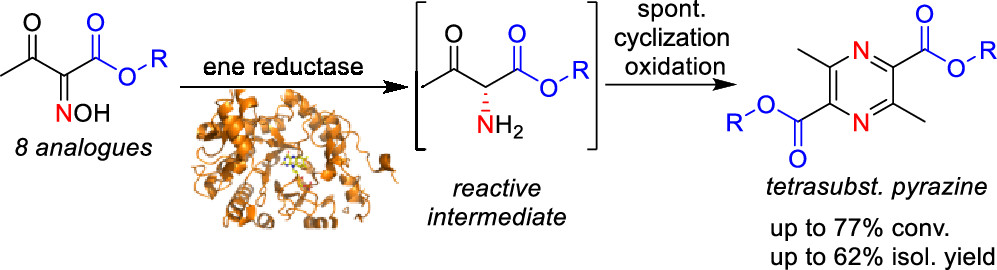
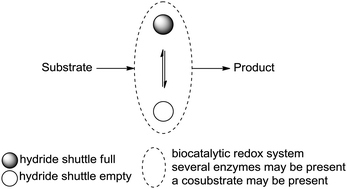
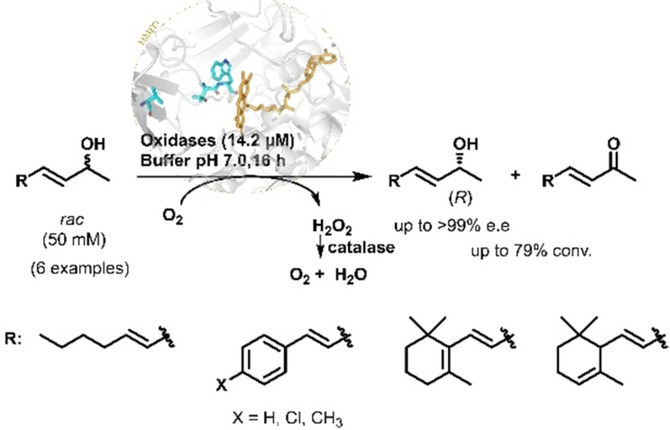
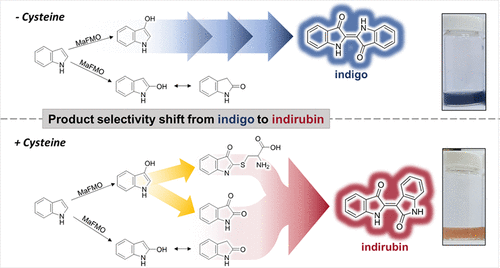
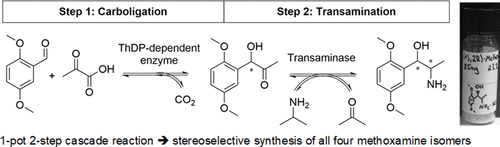

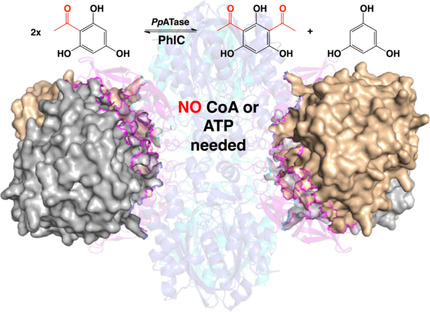
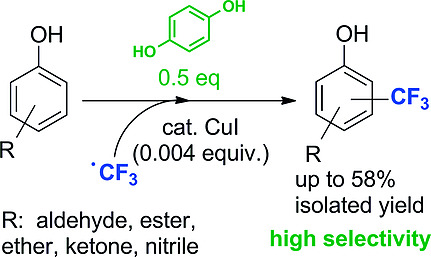
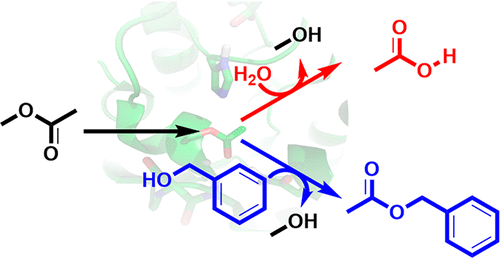
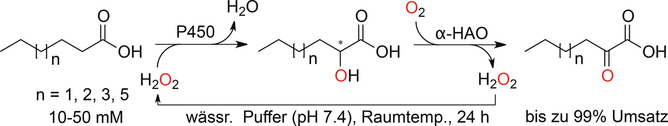
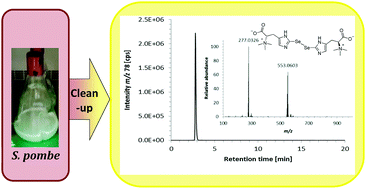
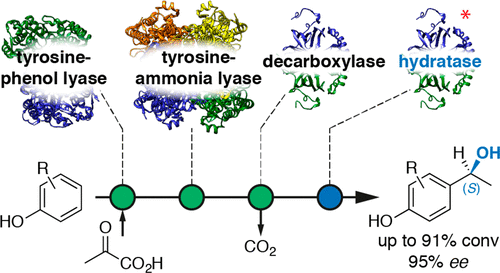
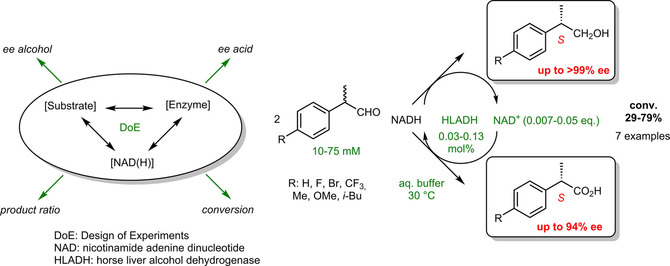
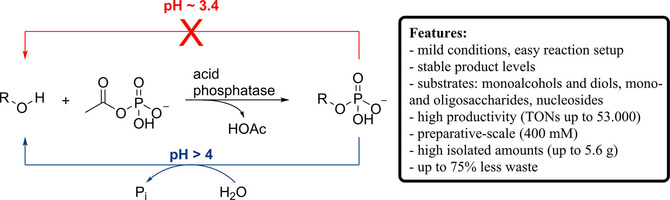
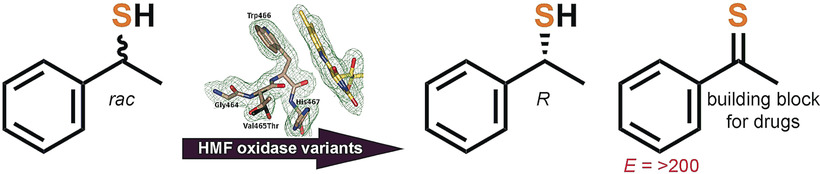
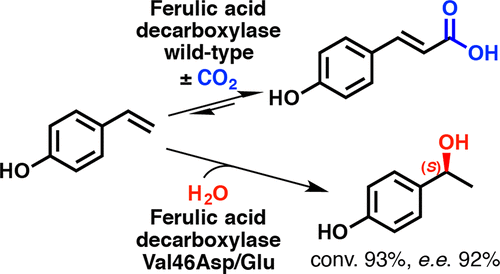
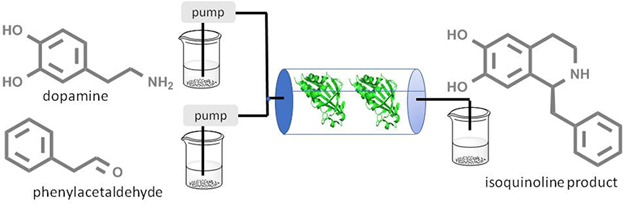
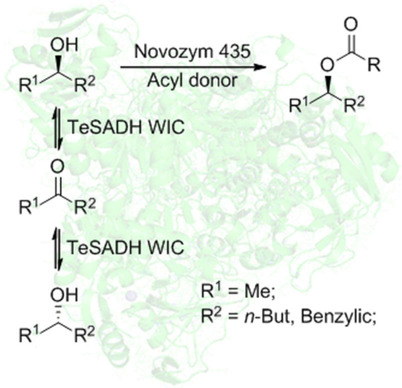
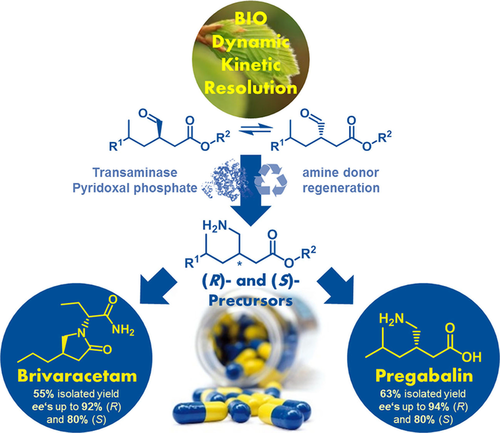
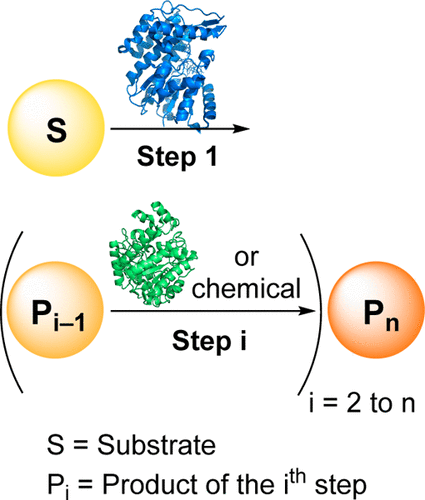
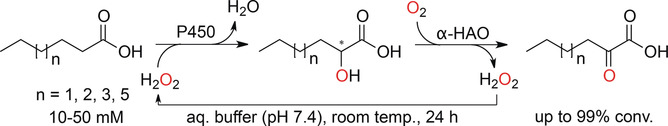
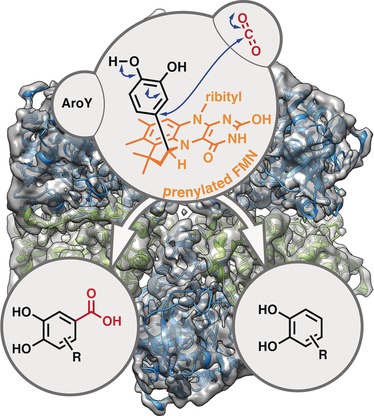
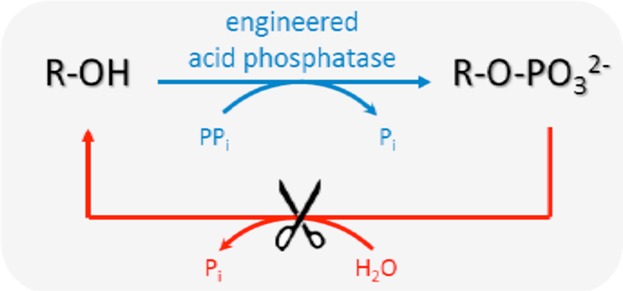
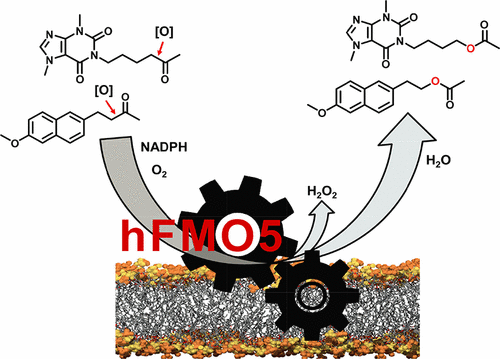
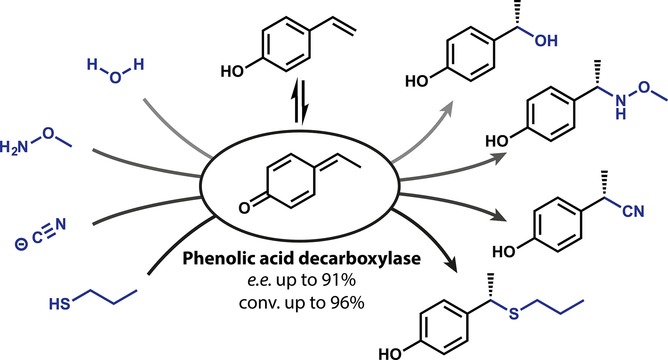
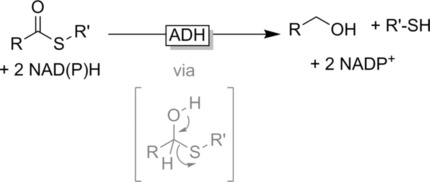
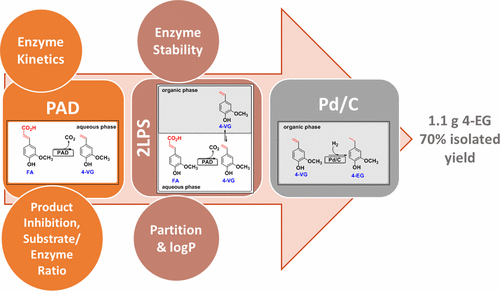
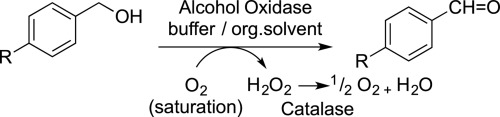
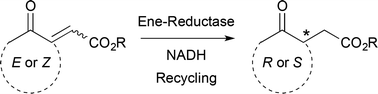
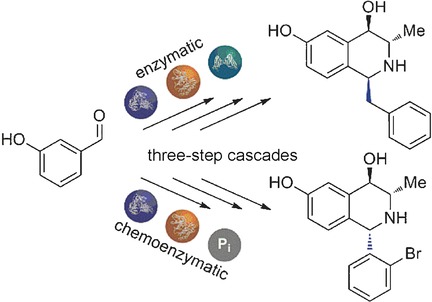
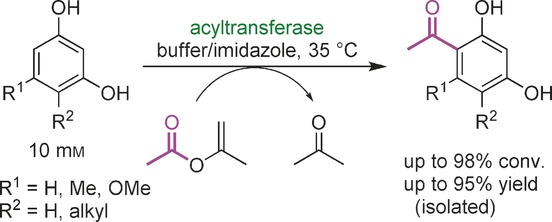
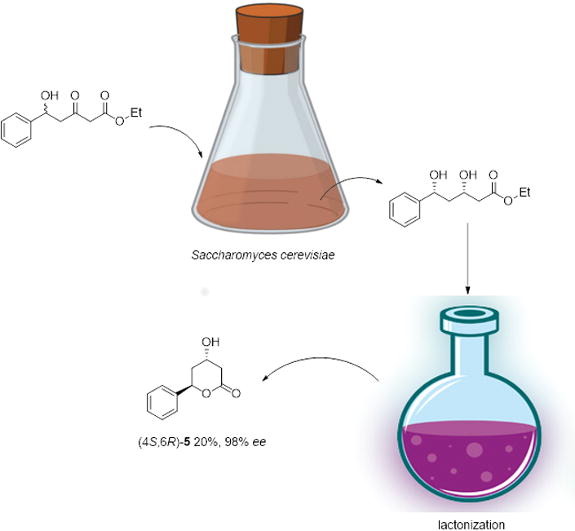
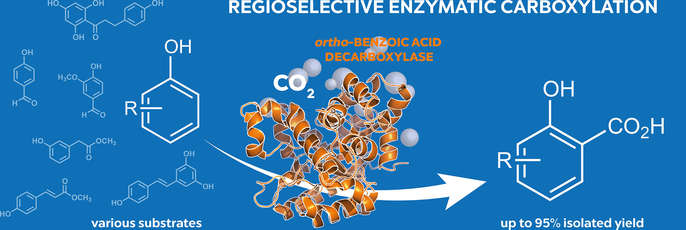
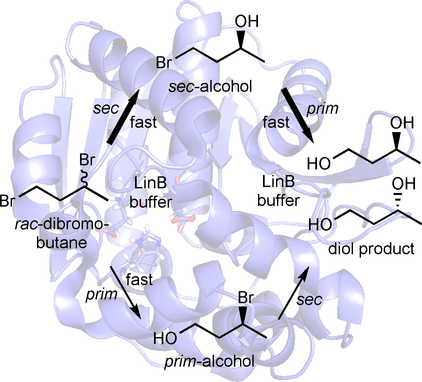
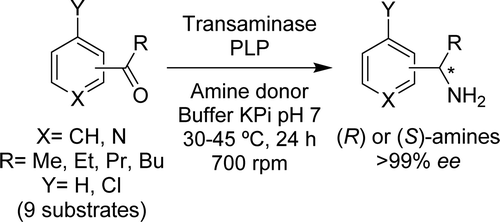
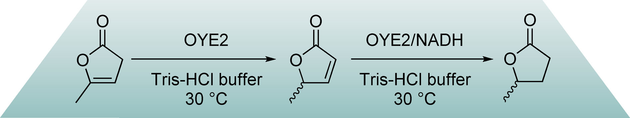
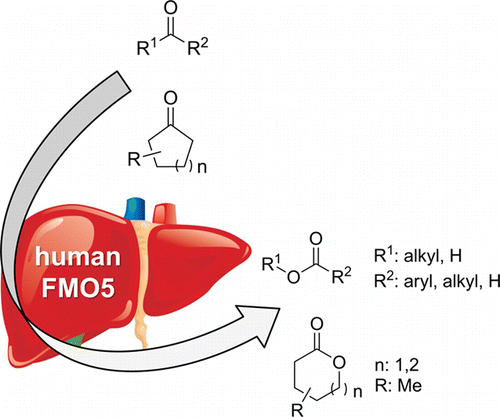
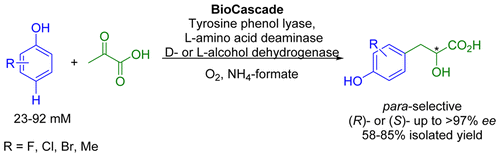
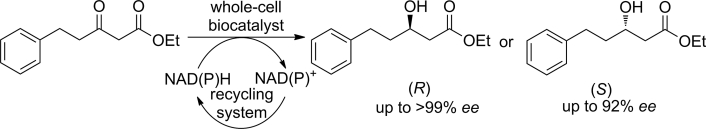
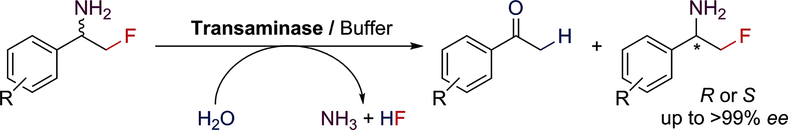
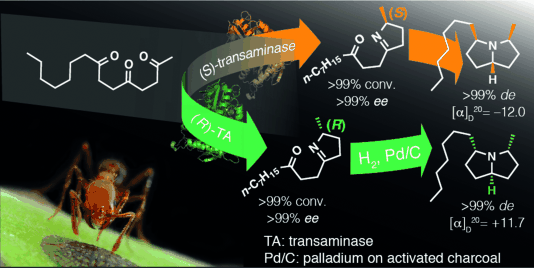
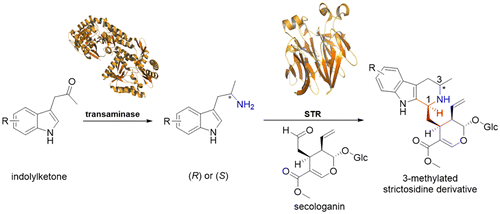
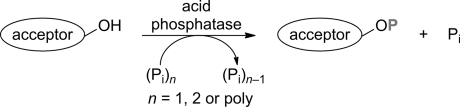
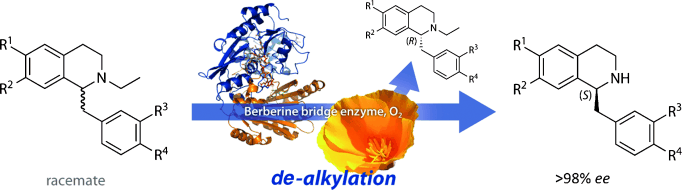
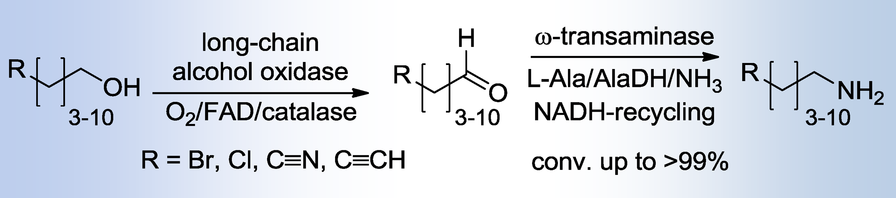
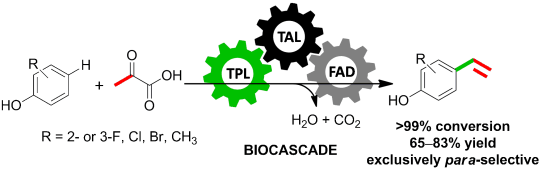
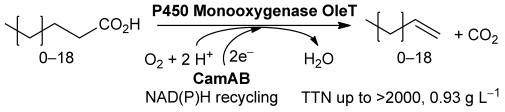
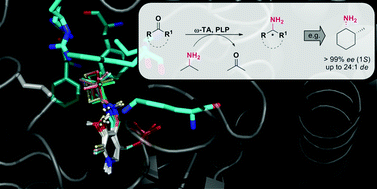
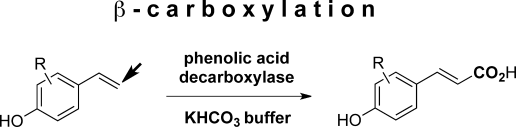
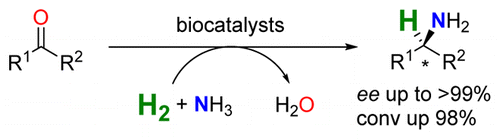

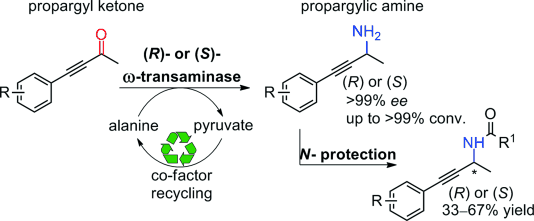
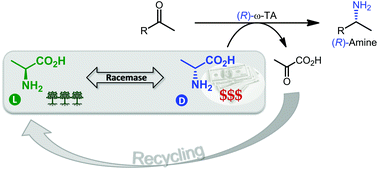



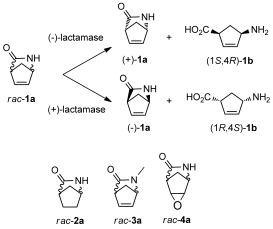
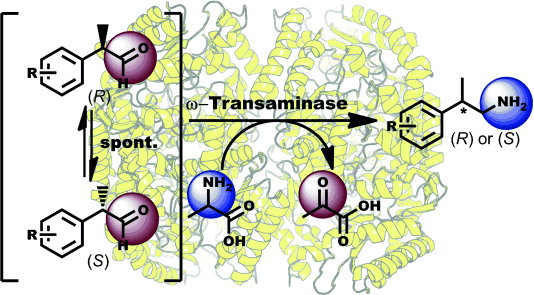
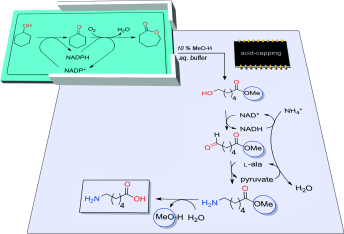
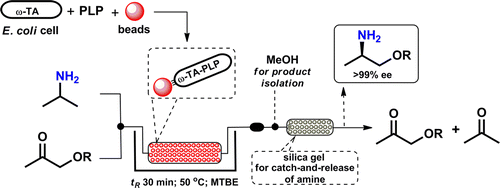
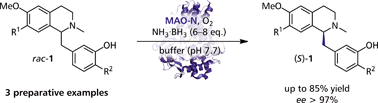
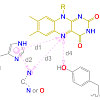
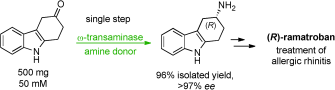
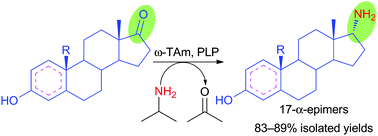
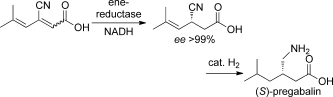
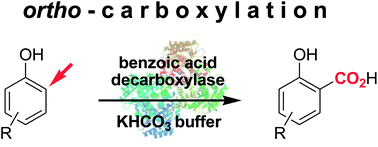

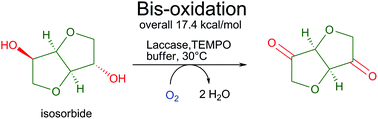
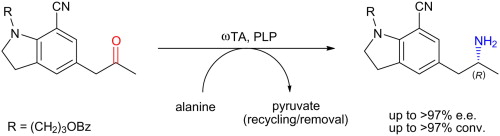


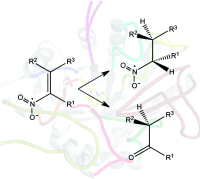
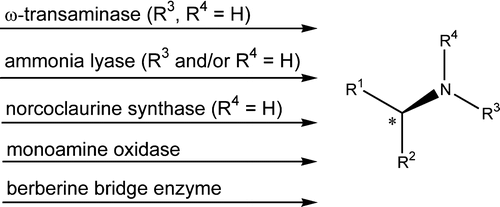
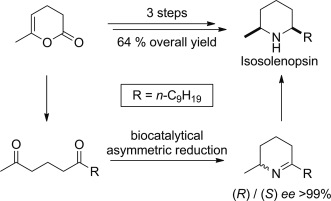
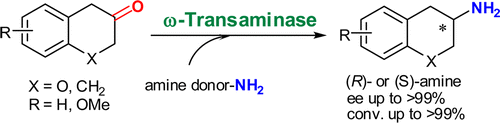

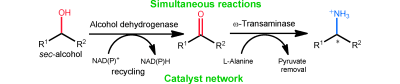
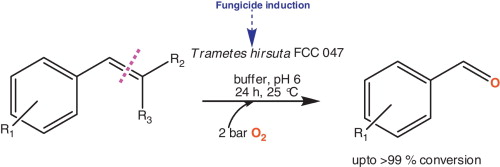
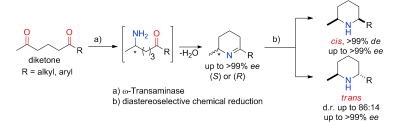
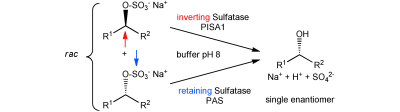

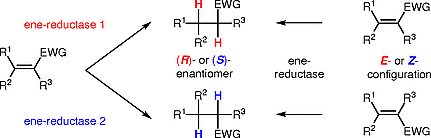
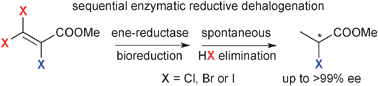
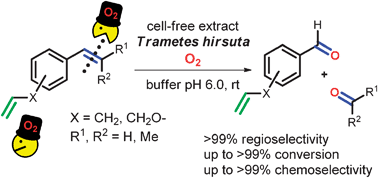
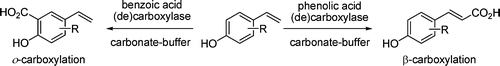
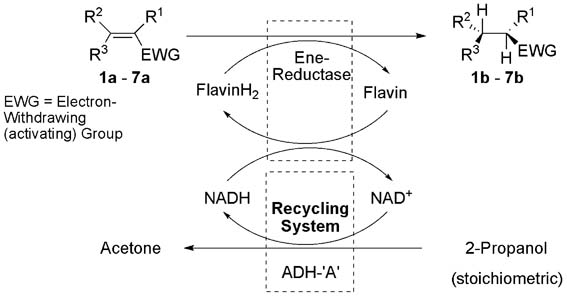
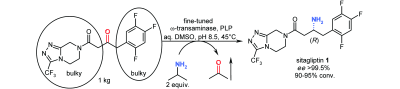
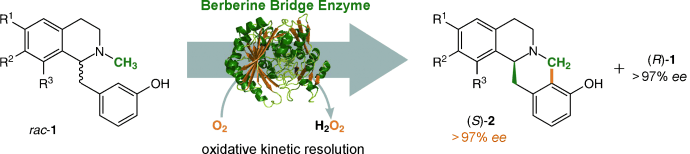
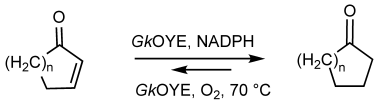
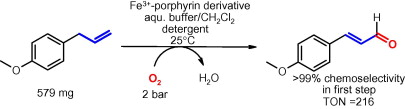
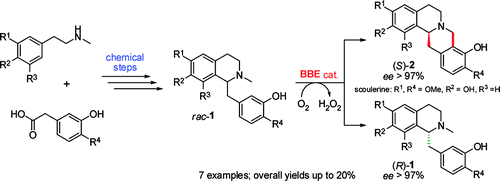
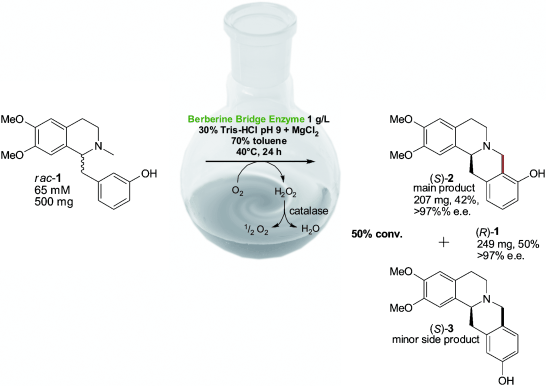
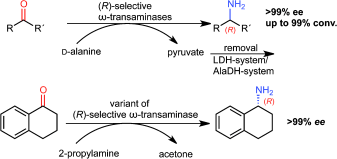
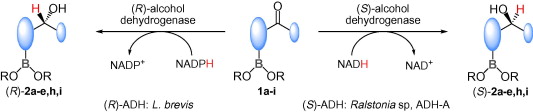
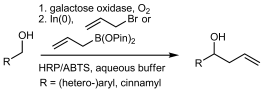
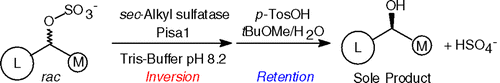
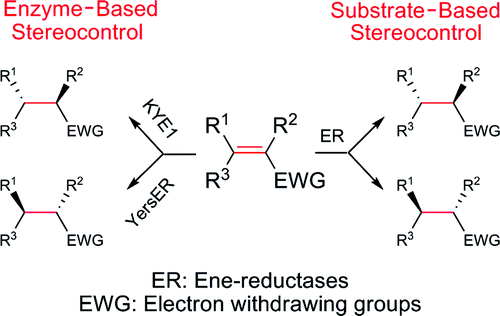
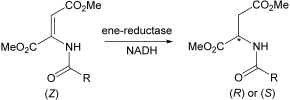
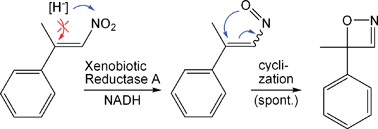
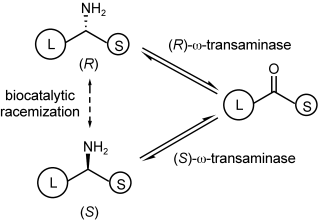
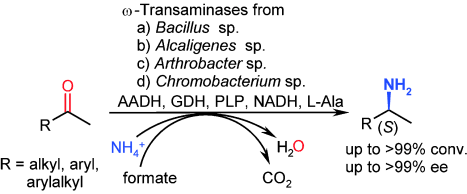
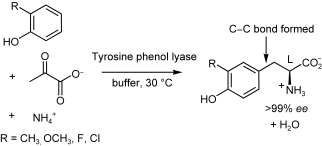
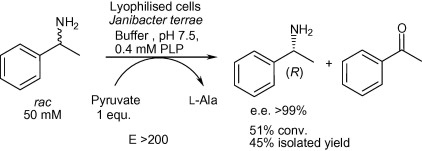
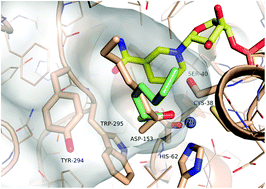
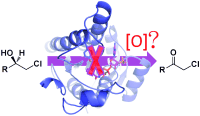
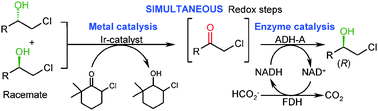
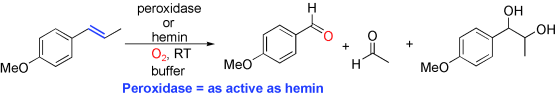
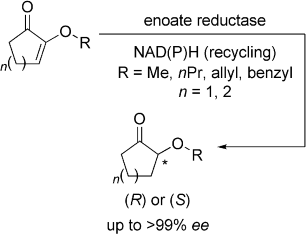
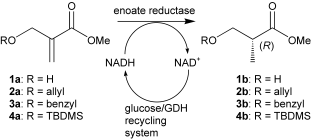
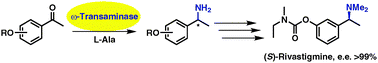

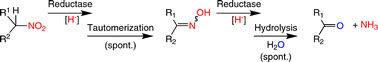
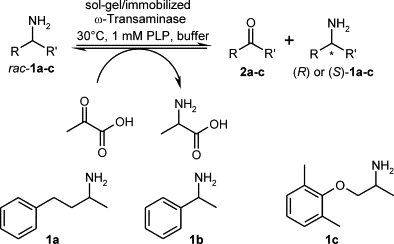
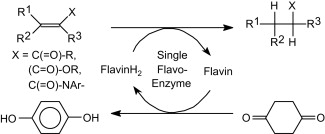
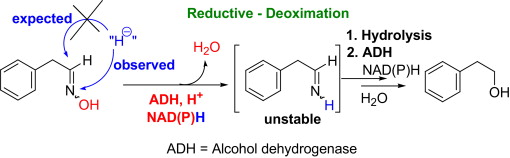
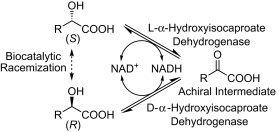
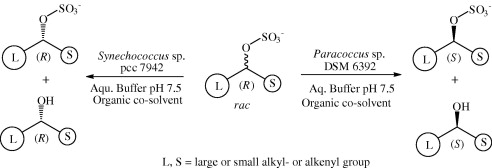
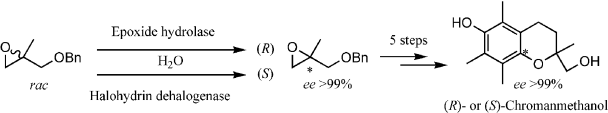
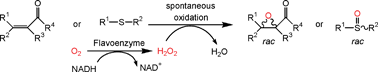
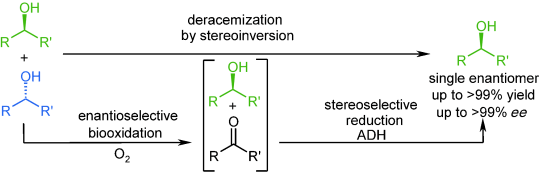
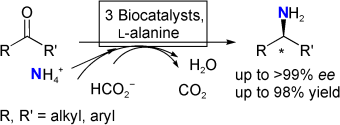
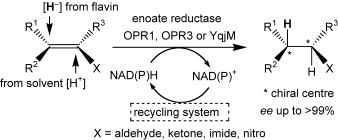

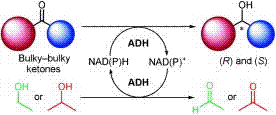
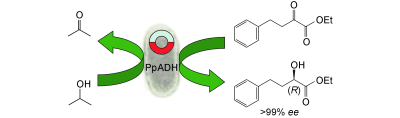
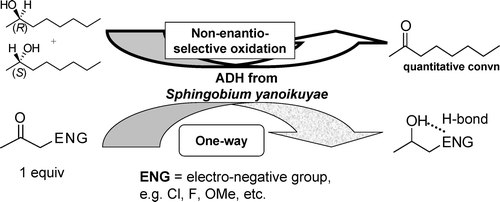
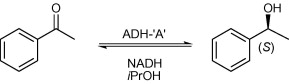
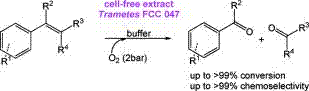
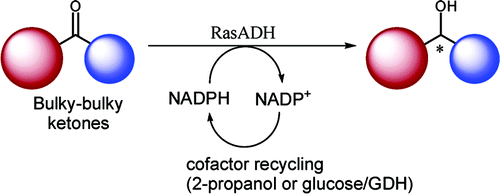
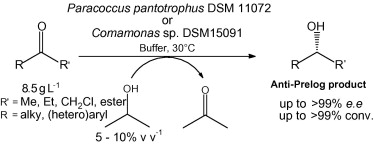
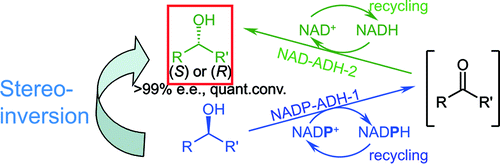
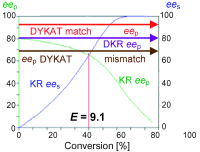
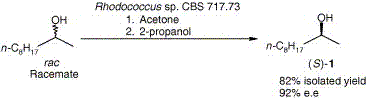
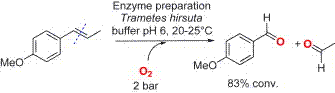
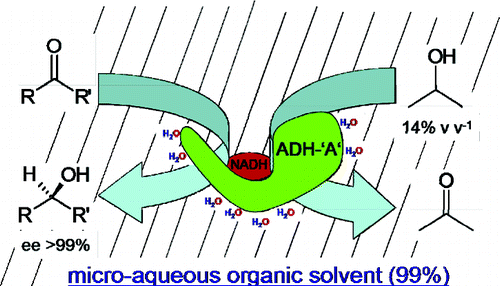
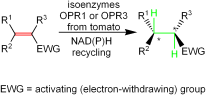
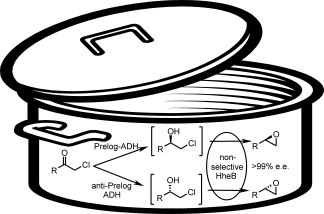

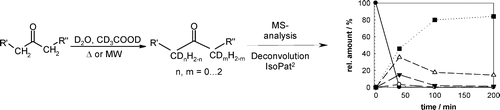
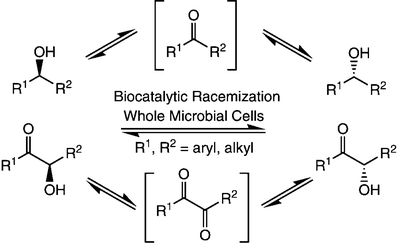
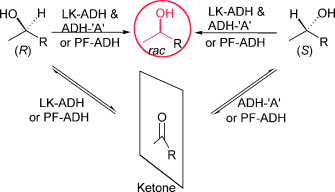
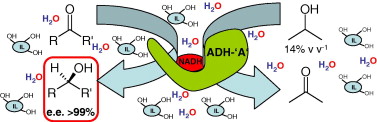

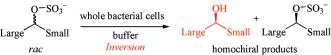
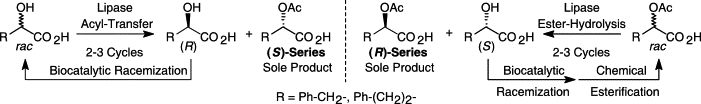
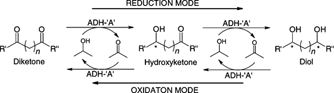

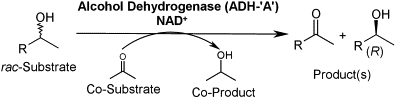
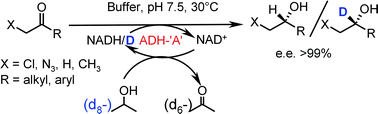
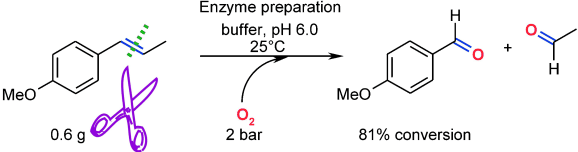
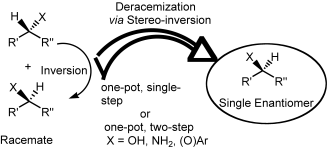
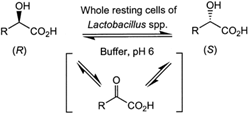

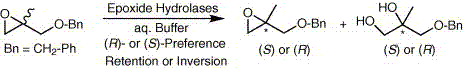
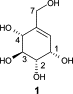

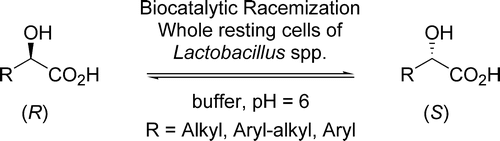

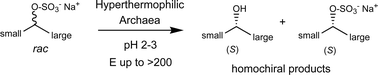
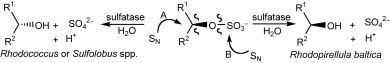
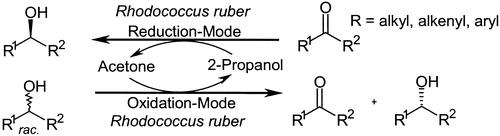
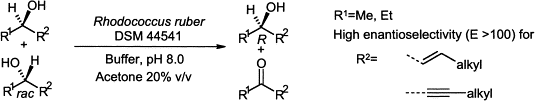
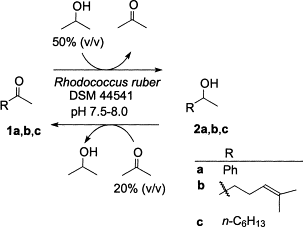

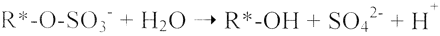
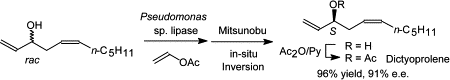
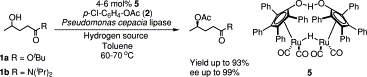
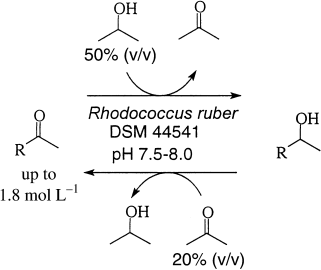
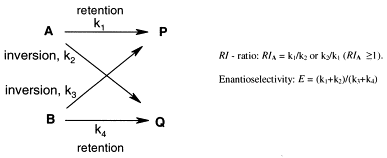
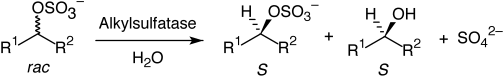
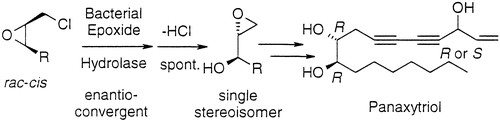
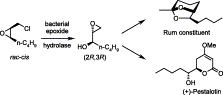
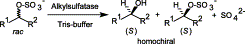
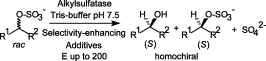

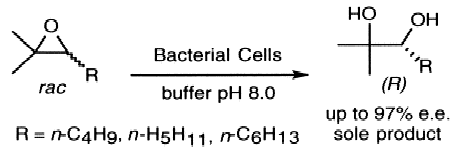
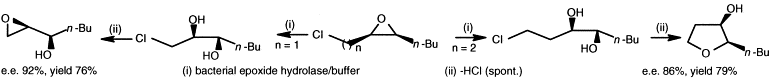
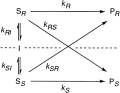

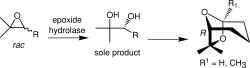
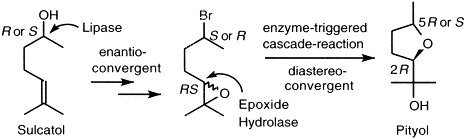
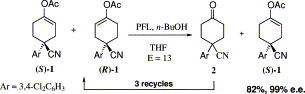
 .
.